Wildlife conservationists sounded the alarm Wednesday as an annual count of monarch butterflies revealed a sharp decline in the number of the iconic insects hibernating in Mexican forests, stoking renewed fears of their extinction.
The annual survey—led by Mexico's National Commission of Natural Protected Areas and the Mexican branch of the World Wildlife Fund for Nature (WWF)—showed a 22% drop in the hibernating monarch population amid accelerating habitat loss driven primarily by deforestation.
"Despite heroic efforts to save monarchs by planting milkweed, we could still lose these extraordinary butterflies by not taking bolder action," Tierra Curry, a senior scientist at the Center for Biological Diversity (CBD), said in a statement.
"Monarchs were once incredibly common," she added. "Now they're the face of the extinction crisis as U.S. populations crash amid habitat loss and the climate meltdown."
Renowned for its epic annual migrations from the northern U.S. and southern Canada to Florida, California, and Mexico, monarchs have suffered a precipitous plunge in population in North America this century.
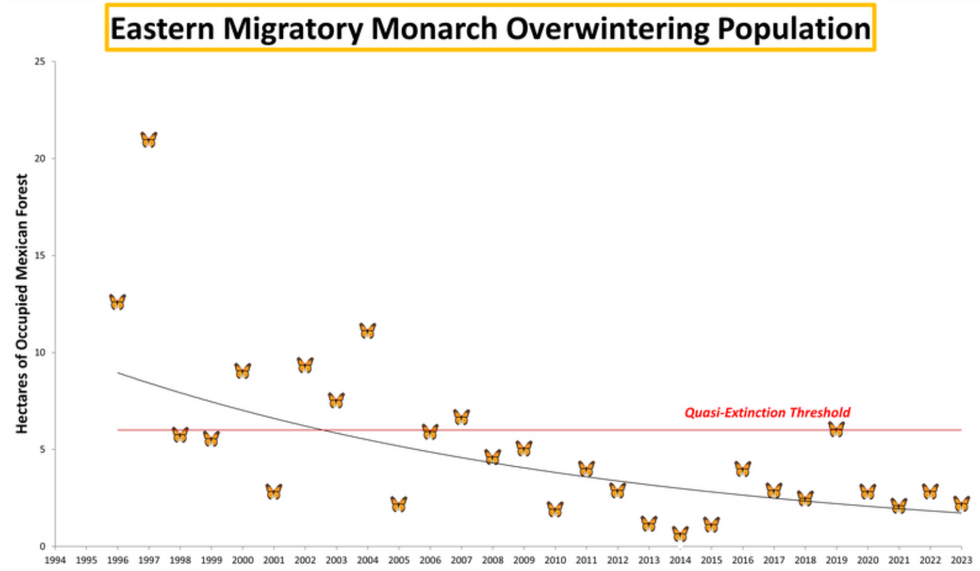
According to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS), the number of eastern monarchs fell from around 384 million in 1996 to 60 million in 2019, and in the West their numbers declined from 1.2 million in 1997 to fewer than 30,000 last year.
As CBD noted:
At the end of summer, eastern monarchs migrate from the northern United States and southern Canada to high-elevation fir forests in central Mexico. Scientists estimate the population size by measuring the area of trees turned orange by the clustering butterflies...The eastern population has been perilously low since 2008.
Last year, the International Union for Conservation of Nature formally listed the monarch butterfly as endangered, citing critical threats posed by the climate emergency, deforestation, pesticides, and logging.
In the United States, the Trump administration in 2020 placed monarchs on the wait list for consideration for Endangered Species Act protection. FWS has until next year to make a final listing determination.
"It is not just about conserving a species, it's also about conserving a unique migratory phenomenon in nature," said WWF Mexico general director Jorge Rickards. "Monarchs contribute to healthy and diverse terrestrial ecosystems across North America as they carry pollen from one plant to another."
"With 80% of agricultural food production depending on pollinators like monarchs, when people help the species, we are also helping ourselves," he added.
This content originally appeared on Common Dreams and was authored by Brett Wilkins.